Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements
List of countries with whom DTAA has been signed.
- Australia
- Bangladesh
- Canada
- China
- France
- Germany
- Japan
- Luxemburg
- Mauritius
- Russia
- Singapore
- UK and USA
Modification in DTAA with Mauritius
- As per the treaty signed in 1983, only Mauritius was allowed to tax capital gains. But generally Mauritius did not impose it. So companies were fully tax exempt. This resulted in large inflow of FDI via Mauritius route (34% of total FDI in India) largely for tax evasion.
- India can now tax capital gains even on a company based in Mauritius. It is also applicable to Singapore treaty.
- It will help in reducing treaty shopping, reduction in opening shell companies in Mauritius and a step towards commitment of BEPS by G20 and OECD.
- Effect- FDI will reduce, round tripping through other tax havens, more reliance on opaque instruments like P-notes.
Liberalized Remittance Scheme
- Under LRS, all resident individuals can freely remit $250,000 overseas every financial year for a permissible set of current or capital account transactions.
- Remittances are permitted for overseas education, travel, medical treatment and purchase of shares and property, apart from maintenance of relatives living abroad, gifting and donations
- Sending money to certain countries and entities is also barred. Under LRS, people can’t send money to countries identified as ‘non cooperative’ by the Financial Action Task Force
- The LRS represents India’s baby steps towards dismantling controls on foreign exchange movements in and out of the country.
- It is a step towards full capital account convertibility.
- It was launched in 2004.
- Negative impact seen in Panama papers case where it was used to buy shares of offshore companies.
Organized Crime
- Organized crime involves carrying out of sophisticated crimes by cartels that have human resources, monetary support and backing of corrupt officials and politicians.
- Examples- drug cartels, hawala money laundering, smugglers, human trafficking, spot fixing of cricket matches, etc.
- The biggest support is from someone in the system which makes action against them difficult.
- Linkage to terrorism- aids and abets terrorism for monetary and other benefit. Plus, they have well established linkages and supply chains in India that can be utilized, international terrorists find it hard to infiltrate- hence can use existing organized crime cartels to carry out their activities. Smuggling and cross-border transactions can also be done for terrorists.
- Measures- NATGRID, CCTNS. India has ratified the UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime for better international cooperation.
Linkages of Development and Extremism
- Lack of development, lack of opportunities and scope to grow in the future leads to frustration. An idle mind is a devil’s workshop. If such a frustration in a country of 65% young people breeds itself, it can cause terrible law and order problems
- Plus, due to illiteracy, people fall for propaganda of extremists. Young people are sometimes immature, have boiling blood and fall prey to romanticization of crime. This leads them to extremism.
- Various other reasons like inter-regional divide, rural-urban divide, caste and ethnic hatred also lead to extremism.
- Eg- LWE and insurgency in north-east.
Naxalism
MHA reduced Naxal affected districts from 106 to 90 and claimed 20% reduction in violence in these areas
Official actions on Naxalism
- Operation Steeplechase in 1970s
- Unified Command in 2010 for inter-state cooperation and start of Operation Greenhunt.
- Security related Infra scheme- LWE affected districts get financial and security-related assistance from the Centre. For example, each district gets minimum Rs 30 crore under the Security Related Expenditure scheme of the Home Ministry.
- Special Infrastructure Scheme, Integrated Action Plan and civic action programme also add to the state’s coffers.
- Road Connectivity Project for Left Wing Extremism (LWE) Affected Areas under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) implemented by MoRD
- 3200 crore invested in Bastar region for roads, railways, bridges as a counter to naxalism
- Samadhan scheme for MHA that deals with coordination, aggressive strategy, intelligence, no financing, etc to tackle Naxal problem.
- Naxal surrender schemes of various states. Eg- Navjeevan Atmasamarpan Yojana of MH
AFSPA
The British had promulgated the Armed Forces Special Powers Ordinance in 1942 to suppress the Quit India Movement
The salient provisions of this act are as follows:
- Governor of the State and Central Government are empowered to declare any part or full of any state as disturbed area if it is in their opinion that it is necessary to prevent terrorist activity or any such activity that might disrupt the sovereignty of India or cause insult to the national flag, anthem or India’s Constitution.
- Section 4 of the act gives special powers to army officers in disturbed area to shoot (even if it kills) any individual who violates law / or is suspected to violate law (this includes assembly of five or more people, carrying of weapons) etc. The only condition is that the officer has to give warning before opening fire.
- Arrest anybody and conduct searches without a warrant, and carry out searches without consent.
- Once a person is taken into custody, he / she has to be handed over to the nearest police station as soon as possible.
- Prosecution of the officer on duty needs prior permission of the Central Government.
SC ruling on AFSPA
- Indefinite deployment of armed forces in the name of restoring normalcy under AFSPA “would mock at our democratic process”, apart from symbolizing a failure of the civil administration and the armed forces.
- It does not matter whether the victim was a common person or a militant or a terrorist, nor does it matter whether the aggressor was a common person or the state. The law is the same for both and is equally applicable to both.
- There is no concept of absolute immunity from trial by a criminal court if an Army man has committed an offence
Overall, the AFSPA and government actions go hand in hand. Using only AFSPA with no governmental effort for development or pacifying the insurgents has resulted in AFSPA being in force but with no effect.
NATGRID
- NATGRID is the integrated intelligence grid connecting databases of core security agencies of the Government of India to collect comprehensive patterns of intelligence that can be readily accessed by intelligence agencies.
- NATGRID is an intelligence sharing network that collates data from the standalone databases of the various agencies and ministries of the Indian government.
- It is a counter terrorism measure that collects and collates a host of information from government databases including tax and bank account details, credit card transactions, visa and immigration records and itineraries of rail and air travel.
- This combined data will be made available to 11 central agencies, which are: Research and Analysis Wing, the Intelligence Bureau, Central Bureau of Investigation, Financial intelligence unit, Central Board of Direct Taxes, Directorate of Revenue Intelligence, Enforcement Directorate,
Narcotics Control Bureau, Central Board of Excise and Customs and the Directorate General of Central Excise Intelligence
- It can provide the real time tip-offs and predictive intelligence to deal with the terrorist threat. It will help to collate scattered information into a transparent, accessible, integrated grid
Challenges and concerns of NATGRID
- The state police or different defense departments are not mentioned among the 10 “user agencies” who will be able to electronically access 21 sensitive databases.
- NATGRID effectiveness will be reduced if the Central agencies are not willing to share current intelligence with the State agencies.
- NATGRID faced opposition on charges of possible violations of privacy and leakage of confidential personal information.
- NATGRID will have access to all kinds of data under one roof and can also prove to be counter-productive if misused.
National Counter Terrorism Center
Center planning to revive NCTC as a department in IB. It will be a federal counter-terrorism agency just like in USA. It was opposed by states as it would encroach upon their information gathering mechanisms.
Characteristics of National Counter Terrorism Center
- It has the power to conduct searches and arrests in any part of India.
- The NCTC will carry out counter-terror operations and collect, collate and disseminate data on terrorism.
- The agency will also maintain a data base on terrorist and their associates including their families.
- It will have representation from NIA, CBI, RAW, NCRB, etc.
Issues of National Counter Terrorism Center
Some states allege NCTC to be non-federal nature. NCTC will be empowered to search and arrest people without informing the state government, police or antiterror squad in the loop. Its functions overlap with NIA.
Unlawful Activities Prevention Act Amendment 2019
- Govt can designate individuals as terrorists and onus lies on the accused to prove otherwise
- Accused can appeal to govt for removal of name but no time frame for govt to respond.
- More powers to NIA to investigate cases of UAPA
- Activists call this an assault on individual freedom and similar misuse like thst of TADA and POTA
NIA Amendment 2019
- Inspectors of NIA can now conduct raids and investigate terror crimes
- Provision for special courts and additional courts for faster trials
- They can override local police
- The new crimes that can be investigated include offence under Arms Act and Explosives Act, which are seen as impinging on state powers
Nuclear Program of India
- Give brief history- 1974, 1998 pokhran test, no sign on NPT, Pakistan got nuclear weapons in 1998, India inspired confidence and US nuclear deal.
- No First use doctrine. The logic is of deterrence. The enemy should feel that by attacking, the losses are more than the perceived gains.
- India has a cold start doctrine in terms of nuclear weapons.
- It includes a limited attack on Pakistan which would be significant but not big enough to give a reason for Pakistan to launch a nuclear attack. India has denied this doctrine but efforts at reducing the mobilization time like in case of Operation Vijayi Bhava have made it clear that India does follow such a doctrine.
- The criticism is that there is no warranty that if such an attack is done, Pakistan won’t launch a retaliatory strike. Announcing of the usage of TNW, Pakistan is threatening to start a full-fledged nuclear war.
- TNW- used in military operations while SNW used to attack military bases, industry, power plants, etc.
- It is because the difference between TNW and SNW is academic, a nuclear weapon causes mass destruction and It will take no time for a limited nuclear response to boil down into a nuclear war. An idea between TNW and SNW could be usage of SNW to destroy military settlements in Pakistan.
- 3 stage nuclear program – Pressurized heavy water reactor to fast breeder reactor to thorium based nuclear reactor.
No First Use Doctrine
- Developed after the Pokhran II tests in 1998
- It says no use of nuclear weapons as a means of warfare unless first attacked by an adversary using nuclear weapons
- It works on the policy of deterrance and is limited to retaliation only
- The principle is of MAD which would prevent a nuclear war
- It designates PM or his successor to take decision on use of nuclear weapons
- Effects of withdrawal of this policy- start of 3rd war, use by Pak, MAD, impact on civil nuclear program, reaction from USA China
Permission of a nuclear attack is given by Nuclear Command Authority. The Nuclear Command Authority comprises a Political Council and an Executive Council. The Political Council is chaired by the Prime Minister. It is the sole body which can authorise the use of nuclear weapons.
Militancy in Kashmir
- Major uprising in 1980s by JK Liberation Front and other separatists that led to exodus of Kashmiri Pandits after 1990
- Unrest erupted again in 2010 over control of Amarnath Shrine Board
- After 2014, a policy of zero tolerance for terrorism came up
- Kashmir has two types of terrorist organizations- Home grown include Hizbul Mujahideen while Pakistan sponsored like LeT and Al-Qaeda
- 2016- Burhan Wani killed and all from his Hizbul gang eliminated. This led to extreme violence in valley.
- Use of pellet guns to calm down crowds becomes controversial as the pellets make people blind.
- Operation All Out by Indian Army to flush out terrorists from the valley
- NIA launched investigation against moderates (Hurriyat) and sealed bank accounts that show money flow from Pakistan
- By 2019, most Hurriyat leaders were kept in house arrest
- After revocation of Article 370, Kashmir was kept under heavy military control
Relief measures for Kashmir
- 80000 crore by central government for overall development
- Himayat programme under DDU-GKY and NRLM for skilling Kashmiri youth
- Watan ko Jano program of MHA for exposing Kashmiris to the development and progress in other states.
- People-to-People contact between Kashmir and rest of India.
- Center-state cooperation.
Siachen issue
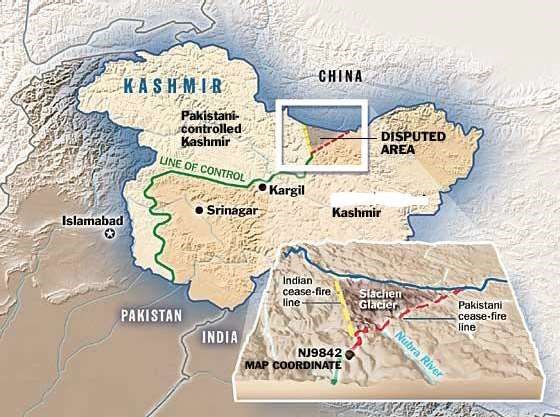
- The Siachen dispute is a direct result of the ambiguity that exists in the Karachi ceasefire agreement of July 1949.. The agreement, which established the ceasefire line, the positions of the two militaries at the end of the 1947-1948 war, did not delineate beyond grid reference NJ 9842.
- Strategic Importance– Siachen sits at a very strategic location with Pakistan on the left and China on the right. It overlooks the Karakoram highway connecting China and Pakistan that gives us a military advantage.
- In 1983, Pakistani generals decided to stake their claim through troop deployments to the Siachen glacier. To pre-empt Pakistan, India launched Operation Meghdoot in April 1984 and occupied the high points of the glacier.
Problems at Siachen
The issue came up when soldiers of Madras Regiment died in February 2016 and one soldier Hanumanthappa succumbed to his injuries.
- 846 military personnel have died at the Siachen glacier between 1984 and 2012.
- Avalanches and the challenging terrain as a whole have been a major reason
- The climatic conditions and sub-zero temperatures lead to illnesses such as memory loss, speech blurring, frostbites, and lung infections.
Favoring Demilitarization
- The loss of lives and the revenue spent on occupying Siachen
- It is suggested that Siachen does not have any strategic significance and cannot be used to stage a military offensive
- China would rather intrude through Leh region than coming through Siachen. So its futile to hold siachen for the fear of Chinese intrusion
- There are enough sophisticated monitoring and sensing mechanisms as well as commercial satellite imagery available today to prevent a surprise Pakistani invasion.
- India is not able to provide proper facilities to soldiers there. Soldiers live in makeshift tents, cook food by kerosene.
- Logistics cost are also too much. The soldiers need to go through base camps for acclimatization. There is compulsory psychiatric treatment for those who have served a term at Siachen.
No Demilitarization
- India dominates the Siachen heights and is in a strategically advantageous position vis a vis Pakistan.
- We have militarily and materially invested in the Siachen region over the years or incur lower casualties than Pakistan
- There is fear of the Chinese presence in the vicinity.
- There would be difficulty in retaking the glacier should circumstances so dictate in future.
- If pak takes the territory, will it be POK or full fledged part of Pakiatan?
- In the event of a future war with India, Pakistan and China could launch a joint operation against India in the Ladakh region using Siachen vacated by the Indian Army.
Probable Solution- Mutual withdrawal after jointly recording current military positions and exchanging them without prejudice to each other’s stated positions.
Cyber Security
India is ranked a high 23rd out of 165 nations in The Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI).
Situation of Indian cyber security
India is a net information importer
- Our information highways point west i.e millions of bits of information of Indians travels west mainly through social media platforms. This shows our reliability on west
- Usage of cheap and old phones and devices still continues leading to problems in providing cyber security.
- There is no national security architecture today that can assess the nature of cyber threats and respond to them effectively.
- In spite of instituting a National Cyber Security Coordinator (2014), lack of coordination among different government agencies
- China’s focus on cloud computing techniques and its ability to hack into systems as a part of national propaganda
Types of digital intrusions
- Espionage: Involves intruding into systems to steal information of strategic or commercial value.
- Cybercrime: Referring to electronic fraud or other acts of serious criminal consequence.
- Attacks: Intended at disrupting services or systems for a temporary period.
- War: Caused by a large-scale and systematic digital assault on India’s critical installations.
Solution of digital intrusions
Govt has decided to set a National Cyber Security Coordination Center NCCC that will coordinate with all intelligence agencies, CERT-in, foreign agencies, monitor cyber security. It will be an arm of CERT-In
Budapest Convention on cybercrime addresses Internet and computer crime by harmonizing national laws and increasing cooperation among nations. This is the only multilateral convention about cybercrime but India is not a signatory since it says US and developed world drafted it without its consultation.
Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
It has been launched by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), in association with National eGovernance Division (NeGD) and industry partners, to strengthen Cyber security ecosystem in India. It is first public-private partnership of its kind and will leverage the expertise of the IT industry in cyber security.
Data (Privacy and Protection) Bill, 2017
- Rights-based approach where consent of individual is mandatory for collection, processing, storing and deletion of personal data with very limited exceptions on case-by-case basis.
- Differentiate data collectors and data processors and mandates that they shall collect, store or access personal data in a lawful and transparent manner and implement necessary security measures for data collected
- Data intermediaries must inform individuals of data breach within a time frame
- Creation of position of data protection officer for grievance redressal of end-users with a provision for appeal to Data Privacy & Protection Authority
- The only drawback is that when data is stored outside India, there is no jurisdiction of this law.
Draft Geospatial Information Regulation Bill 2016
- Geospatial imagery or data acquired through space or aerial platforms such as satellite, aircrafts, airships, balloons, UAVs. Graphical or digital data depicting natural or man-made physical features, phenomenon or boundaries of the earth
- It now requires government permission for acquiring, disseminating, publishing or distributing any geospatial information. A Security Vetting Authority will be established for the same.
- Illegal acquisition, dissemination, circulation outside India, wrongful depiction of India’s map will acquire fines ranging from 1 crore to 100 crore and up to 7 years of imprisonment.
- Pakistan objects because now its compulsory to show entire J&K as part of India.
- Limitations- New app developers will be restricted while people outside the country will have no such limitation. Larger companies have money to go through security vetting, but upstarts may not have it.
SECURITY FORCES
Paramilitary comes under Home Ministry while Army comes under Defence ministry.
The Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) refers to
- Assam rifles: It came into existence in 1835. It has functions of counter insurgency and border security operations along Myanmar border.
- Border Security force: It came into existence after 1965 India-Pakistan war. It is the primary border security force of India manning western borders of India.
- Central Industrial Security Force: It was set up in 1969. It is the largest such force in the world. Its job is to provide security to various PSUs and commercial places.
- Central Reserve Police Force: It was set up in 1939. It is the largest central armed police force in India. It looks after internal security in India like naxal operations. It also helps with UN peacekeeping missions.
- Indo-Tibetan Border Police: It was formed after India-China war in 1962. It guards the China border. It is also trained in disaster management, UN peacekeeping etc.
- National Security Guard: It combats terrorist activities and also internal disturbances in States.
- Sashastra Seema Bal: It was established in 1963 and guards Nepal and Bhutan borders. It also helps control anti-national activities at these borders.
Bharat Ke Veer– The portal is an IT based platform, with an objective to enable willing donors to contribute towards the family of a martyred soldier.

![UPSC CSE Topper Mains Answer [Part 3] images-2023-06-17T192506.595](https://iasbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/images-2023-06-17T192506.595-150x150.jpeg)

![UPSC CSE Topper Mains Answer [Part 1] images-2023-06-17T191749.185](https://iasbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/images-2023-06-17T191749.185-150x150.jpeg)
![Ancient History Notes for UPSC [Part 7] Mauryan Empire slide_3_compress34](https://iasbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/slide_3_compress34.jpg)




![Disaster Management UPSC Notes - [Important Topics Covered] images-23](https://iasbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/images-23-150x150.png)