• The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) is a military partnership made up of the United States, Canada, and several countries in Western Europe. It was created by the North Atlantic Treaty (also called the Washington Treaty) in April 1949.
• There are 31 member states right now.
Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States were the first countries to join.
Greece and Turkey signed the treaty in 1952, West Germany in 1955 (which became Germany in 1990), Spain in 1982, the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Poland in 1999, Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia in 2004, Albania and Croatia in 2009, North Macedonia in 2020, and Finland in 2023.
France left NATO’s combined military command in 1966, but it stayed a member of the group. In 2009, France took its place back in NATO’s military command.
o Sweden has recently shown that they want to join NATO.
• Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium.
• The Allied Command Operations’ headquarters are in Mons, Belgium.
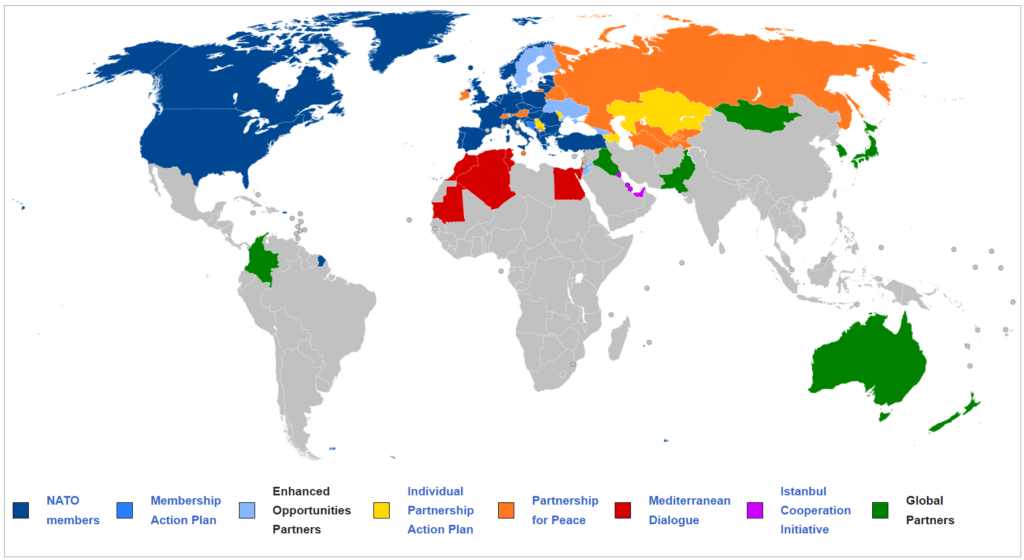

Table of Contents
The goals of NATO
• The main and long-term goal of NATO is to protect the rights and safety of all of its members through political and military means.
Political goals: NATO supports democratic values and gives its members the chance to talk to each other and work together on defence and security issues to solve problems, build trust, and, in the long run, keep wars from happening.
Military Goals: NATO wants to make sure that problems are solved peacefully. If diplomatic attempts fail, it has the power to use the military to deal with the situation.
o These are done under the collective defence clause of NATO’s founding treaty, Article 5 of the Washington Treaty, or under a United Nations mandate, alone or with other countries and international organisations. o NATO has only used Article 5 once, on September 12, 2001, after the 9/11 attacks on the US World Trade Centre.
Minimum Requirements for NATO Membership
• All of Europe’s new democracies that agree with the alliance’s beliefs and are ready to take on the responsibilities of membership could join NATO.
• There is no membership check list.
• People who want to join must meet these five requirements:
New members must support democracy, which includes being open to differences.
New members must be making progress towards a market economy, and their armed forces must be under firm civilian control.
They need to be good neighbours and accept the sovereignty of other countries outside of their own.
They need to work towards being able to work with NATO troops.
• Again, these criteria are important, but they are not a tick list that immediately leads to membership in NATO.
• All of the present members must agree to invite new ones.
• When deciding whether to call new members, the ratification process in each member state must be taken into account. In the United States, decisions are made after consulting with Congress.
• The most important factor in deciding whether to invite a new country to join NATO is whether it will strengthen the alliance and help achieve the main goal of NATO expansion, which is to make Europe safer and more stable.
How Does the NATO Work?
NATO has an integrated military command system, but very few of its forces or assets are its own. Most forces stay under full national command and control until member countries agree to take on NATO-related tasks.
• All 30 allies have an equal say; the Alliance’s decisions must be unanimous and agreed upon by all members; and the Alliance’s members must respect its core values, which are democracy, individual freedom, and the rule of law.
• NATO does not protect its members during civil wars or coups that happen inside their own countries.
The members of NATO pay for it. About three-quarters of NATO’s spending comes from the U.S.
Why did NATO Originate?
• At the end of World War II in 1945, western Europe was both economically and militarily weak. This was because the western Allies had quickly and drastically cut their armies.
• The Marshall Plan was started by the United States in 1948. It gave a lot of money to the countries of western and southern Europe on the condition that they work together and plan together to speed up their own recoveries.
As for military healing, in 1948, the United Kingdom, France, and the Low Countries (Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg) signed a treaty called the Brussels Treaty. Under this treaty, they agreed to work together to protect themselves. This agreement is called the Western European Union.
Soon, though, it became clear that a stronger alliance would be needed to give the Soviets a strong enough armed counterweight.
o In March 1948, after what was almost a communist coup d’état in Czechoslovakia in February, the three countries started talking about a plan for collective defence that would make the West safer and support democratic values.
France, the Low Countries, and Norway joined these talks in the end, and in April 1949, they led to the North Atlantic Treaty.
• At the end of World War II, ties between the US and the USSR got worse and worse, which led to the Cold War.
The USSR wanted to increase its power in Europe by spreading communism, but the US saw the USSR’s ideas as a threat to its way of life.
• In 1955, as the Cold War was heating up, the Soviet Union signed the Warsaw Pact with socialist countries in Central and Eastern Europe. The Pact was seen as a direct strategic counterweight to NATO because it was mostly a political and military union.
It was made up of Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Albania, which left in 1968.
The Pact was officially broken up in the beginning of 1991, after the Soviet Union broke up.
What are NATO’s alliances?
• NATO is a part of three groups that give it more power outside of its 31 member countries.
Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC): This is a group of 50 countries that meet to talk about political and security problems and get advice from each other.
o It sets the overall political framework for NATO’s cooperation with partner countries in the Euro-Atlantic area and for the bilateral ties built between NATO and each partner country through the Partnership for Peace (PfP) programme.
The Partnership for Peace (PfP) is a programme of practical bilateral cooperation between individual Euro-Atlantic partner countries and NATO. It allows partners to build their own relationships with NATO and choose their own objectives for cooperation.
o The North Atlantic Cooperation Council (NACC), which was set up in 1991 after the end of the Cold War, was replaced by the East Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC) in 1997.
Mediterranean Dialogue is a partnership forum that aims to add to security and stability in NATO’s Mediterranean and North African neighbourhood and to support good relations and understanding between participating countries and NATO Allies.
o At the moment, Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia are the non-NATO countries that take part in the Dialogue.
The Istanbul Cooperation Initiative (ICI) is a partnership forum that aims to add to long-term global and regional security by giving non-NATO countries in the wider Middle East region the chance to work with NATO.
o Right now, the Initiative is made up of Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates.
NATO Plus
It is a group made up of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) and five other countries: Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Israel, and South Korea. The goal of the group is to make it easier for countries to work together on defence around the world.
• If India joined NATO Plus, the countries would be able to share information more easily. This would be good for India.
India would have quick access to the most advanced defence technology.
It would make India’s military relationship with the US even stronger.
• Benefits for the US: By adding India to NATO Plus, security arrangements would build on the close relationship between the US and India to improve global security and stop the CCP from getting aggressive in the Indo-Pacific area.