Criminalising the act of Beggary — Unconstitutional
The Delhi High Court has strike down the provisions of the law which sanction punitive action against beggars (including imprisonment) as unconstitutional.
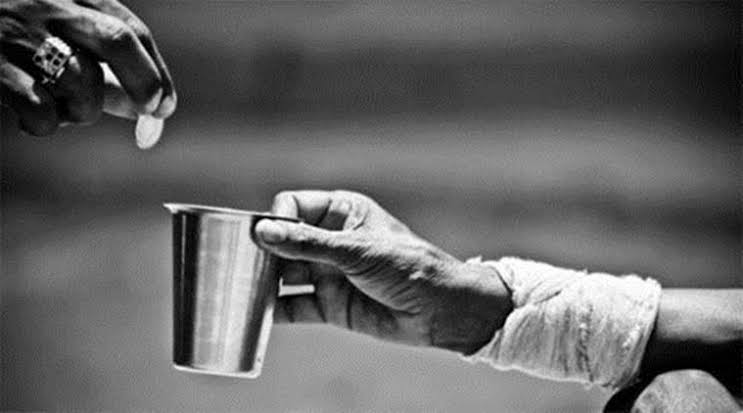
Poverty cannot be a crime!
This is an excellent example of Judicial Activism
The Transgender Persons Bill, 2018 — criminalises the act of beggary by the transgender persons — can be imprisoned and fined
Colonial legacy:
- Bombay Prevention of Begging Act, 1959
- Targeting of allegedly “criminal tribes” in British colonial territories
- Criminal Tribes Act — britishers believed that there are groups of communities which are criminal by birth, nature, and occupation.
- The Act unleashed a reign of terror, with its systems of surveillance, police reporting, the separation of families, detention camps, and forced labour.
- Criminal Tribes Act was replaced by Habitual offenders Act 1952
| Misuse of Begging Act — On the eve of Common Wealth Games 2010, Delhi government took beggars off the streets lest their presence embarrass the nation in the eyes of foreigners.Regular part of preparing for national events, such as Independence Day and Republic Day. |
Delhi HC’s Observations —
- Court has sought to dispel the idea of begging as a disease — which leads to its stigmatisation and criminalisation — and to regard it as a symptom.
- The underlying disease is the failure of the state to protect citizens who fall through the social security net.
- Criminalising begging attacks the fundamental right of the most vulnerable, the poorest of the poor, to regain access to basic necessities like food and shelter.
- The real problem is of organised begging rackets will have to be addressed by other means, perhaps based on the law of trafficking.
Way Forward —
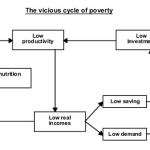
- Poverty should not be considered as a crime, rather it sought for protection.
- There is a need to reduce the rising inequalities and move towards egalitarian society
- A way to tackle this can be — spending aggressively on rehabilitation
==> The Delhi high court’s judgment reinforces the values of inclusiveness and tolerance in Indian society through its references to the principles of equality, liberty and dignity.