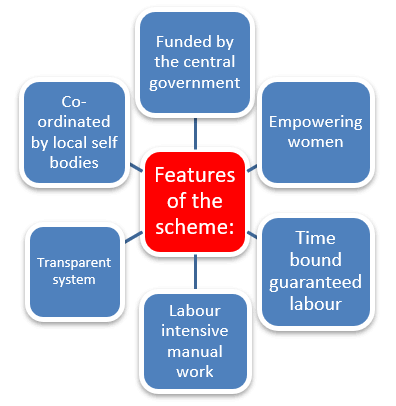
Table of Contents
Key Issues of MGNREGA Scheme
- Design Issues
- Low Wage Rate — 17 states have less than corresponding minimum wage
- Insufficient budget allocation
- Over-Centralisation — at the cost of PRI | Real-time Management Information System and Centralised Payment System | this also negatively affects the grievance redressal
- 60-40 ratio between wages-material
- Penalisation of the workers — centre withholds the wage payment for workers of states that don’t meet the admin requirement like submission of audit receipts within the stipulated time
- Operational Issues
- Payment Delays
- Leakages and siphoning — esp prior to DBT and JAM
- Non-Payment of unemployment allowances — despite MIS shows them but there is inaction at the centre’s part
- Poor Asset quality
- Maladministration — eg. in Jharkhand, instances of genuine job card being randomly deleted to meet 100% DBT implementation targets.
REFORMS of MGNREGA Scheme
- New works — MGNREGA 2.0 — 30 new work areas have been added
- Asset Quality — states took target towards durable assets — 60-40 ratio @district level (instead of panchayat level)
- Better Monitoring — GPS | GIS | Geotagging
- Reduced Delays in wage payments — NeFMS (National electronic Fund Management System)
- Budget Allocation — increment
- Skill Development
- Strengthening the social auditing culture | training the personnels to reduce corruption and enhance accountability
- Expanded entitlement — from 100 to 150 days @drought affected areas
MGNREGA — Reforms needed amidst COVID-19
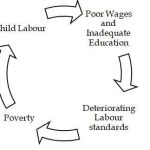
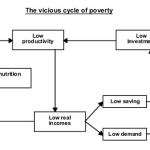
- Amidst economic crisis triggered by COVID-19, a record 5 crore persons from 3.5 crore households sought work under MGNREGA.
- Whenever at any place, employment under MGNREGA rises — its a bad sign for the level of economic development
- Any rise in MGNREGA means there is a drought of jobs and incomes. Here, it is the massive influx of migrant labourers who returned from various states.
- UP has seen a 300% rise in May 2020, compared to May 2019. This is troubling
Why reforms are required in MGNREGA Scheme ?
- Permitted Work List expansion in MGNREGA Scheme
- As of now, there is a prescribed list of work areas which can be permitted under MGNREGA, eg. digging up pits, planting plants etc. This in a way restrict the extent of useful work to be offered.
- Now its being mooted that this list be opened up and become more liberalised. Why can work under national highway or railway be undertaken under MGNREGA — this way useful work will be done, compared to present useless work, just for the sake of fulfilling the MGNREGA mandate.
- Any public work ultimately required labour and so long as it is given on demand, MGNREGA fulfils its purpose.
- Given the massive demand of labour under MGNREGA, it is right time to open up its work area.
- The 60-40 divide in MGNREGA Scheme
- As of now, it is mandated to maintain a 60-40 ratio between wages and material cost. This means majority of the funds must be used for giving out wages rather than getting quality material. This was done because of the rise of commission and bribery to procure material by the officials, at the cost of giving wages to people in need.
- Now it is being argued that because of this 60-40 rule, the quality of work done under MGNREGA is poor, as the material cost is restricted — poor quality material.
- Thus the second reform is to allow relaxation to this 60-40 rule under MGNREGA, if it can ensure quality and durable work being done.









![UPSC CSE Topper Mains Answer [Part 2] images-2023-06-17T192027.770](https://iasbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/images-2023-06-17T192027.770-150x150.jpeg)


![UPSC CSE Topper Mains Answer [Part 3] images-2023-06-17T192506.595](https://iasbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/images-2023-06-17T192506.595-150x150.jpeg)
