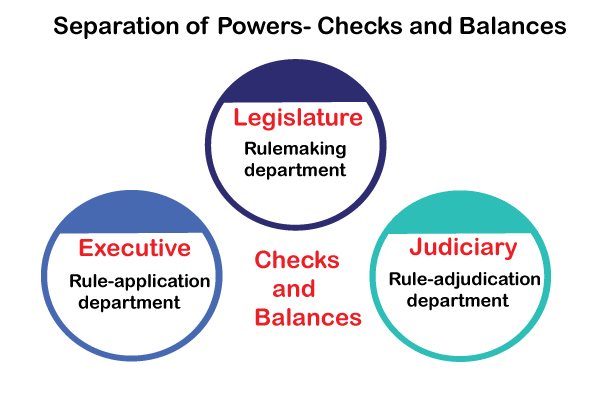
Separation of Power
Introduction
- It means exe, legislative & judicial powers of Govt shd be divided into diff branches & not concentrated in one.
- 1st propounded by Montesquieu in “The spirit of laws”
- Part of Basic structure—KBC (1973)
- Functional separation—Art 50, 121 & 211, 122 & 212, 361
India vs USA
- US–Watertight SoP (Due to Presidential system)
- Indian constitution embraces idea of SoP in an implied manner—Reasonable & flexible SoP—Principle of “Checks & balances”
-
- Bcz of Parliamentary Govt– India does not follow an Absolute separation– Exe is part of legislature & also is responsible to legislature + courts can strike down unconstitutional amendments made by legislature.
-
Objectives
- To ensure that diff branches of Govt shd work autonomously with minimal interference from others.
- Reduces over-centralisation of power in any branch + ensure checks & balance
Importance of SoP
- Imperative for smooth functioning of vibrant democracy–checks & balances prevent abuse of power
- GRM through Independent judiciary.
- Executive remains A/C to Leg for implementation of policies
- Rule of law + Checks arbitrariness
Functional Overlap
- Overlapping Powers Of Legislature
|
With Judiciary |
With Executive |
|
|
- Overlapping Powers Of Executive
|
With Judiciary |
With Legislative |
|
|
Judicial pronouncements
- KBC — SoP is part of basic structure
- Indira Gandhi vs Raj Narain– In Indian Const, there is SoP in a broad sense only—A rigid SoP as in America does not apply to India
Venkaih Naidu—All 3 organs should respect “jurisdictional sanctity enshrined in Const instead of arrogating to themselves a sense of supremacy”.