Role of Civil Society in Developmental Process
- “3rd sector” (After Govt & commerce) in Dev process— Influences Policy-makers & businesses
- Democracy & civil society are twins, integrally related to each other.
- India has a long history of civil society based on the concepts of “daana” means giving and “seva” means service.
- In Gandhian values of volunteerism, During INM—VOs like handloom weavers co-op
- Crucial role in G.G— Act as interface b/t Govt & governed—
- Creation of “Social Capital” + Ownership through engagement– “Jan Bhagidari”
- Watchdog—against violation of HRs & governing deficiencies
- Advocate (PGs)—Of weaker sections, MKSS (RTI)
- Agitator — on behalf of aggrieved citizens.
- Educator — of citizens on their rights, entitlements & R/S & Govt about the pulse of people.
- Service provider — to areas & people not reached by Govt
- Mobiliser — of public opinion
- Social audits, RTI etc
- Civil Society Window (2004)—To enable people to engage with Planning Commission and offer the benefit of their field experiences.
- Constructive & collaborative engagement with civil society is imperitive for for Inclusive, equitable & sustainable Dev & making Dev a “Jan Andolan”
National Policy on Voluntory sector 2007
- Objectives–
- To encourage, enable & empower an independent & effective voluntary sector by creating an Enabling Env
- Creating an enabling Env for VOs + Enable them to mobilize necessary financial resources
- Est Rel b/w Govt & Voluntary Sector on basis of Principles of mutual trust & respect and with shared R/S.
- Issues–
- Most of policies envisaged r not implemented. Ex–National accreditation agency for NGOs has not been formed
Role of NGos in Development
Introduction—
- Non-profit groups which pursue purposes of public interest & works independently of Govt
- To Supplement Dev efforts of Govt—> Welfare state (DPSPs) —> S-E Democracy
Importance of NGOs in Governance
- Collaborative, Participatory & Effective Gov + Holistic Dev & Inclusive Dev Process + Making Dev a “Jan andolan”
- Good Gov + Vibrant Democracy—
- ↑ Govt’s A/C— Act as ‘watchdog’ or third party ‘auditor’– By RTI, Social Audit etc
- ↑ QoS delivery at local level
- Vibrant civil society + Building Community Participation
- Formation & capacity building of cooperatives & women’s SHGs
- Acting as a Social Mediator:
- Role in Disaster Mgt– DMA 2005 calls for community based, participatory approach to DM.
- GOONJ— provides relief during Rahat floods in WB, Assam and Bihar
- During COVID-19— Akshaya Patra Foundation, Kashtakari Panchayat—Raised fund to support workers in Pune
Role of NGOs in Policy formulation & Implementation
- Policy Formation–
- UNDP— NGOs have a sig role to augment Resources, connect with public & oversee meaningful policy implementation.
- BRM Committee— They have effective role in implementing Community Dev schemes
- Influenced Govt to bring— EPA 1986, RTI, ICDS, MNREGA, JJ act, FRA 2006
- Their ground research, expertise, Data & reports provides Policy insights—
- IPCC report— influences C.C policies.
- ASER report—Edu policies
- Policy Implementation–Provides committed expertise, Ground experience,
- ↑ Reach & penetration to untouched sections— Better conveying Govt message– Due to their proximity to masses
- UP– Helped in eradicating hesitancy on polio vaccine (seen as planned sterilization)
- Reaching out to tribal people
- Helping migrants in Covid-19
- Vital in areas like— LGBT rights, Mental health, Menstruation etc– More awareness req–
- Shraddha foundation (MH)– For mentally challenged
- Ammada Trust’s “#Giveher5” campaign to provide sanitary napkins, Sacchi saheli
- Saathi, NAZ– For LGBT
- Social influence & Persuasion— NGOs role in ‘Darwaza band’ campaign, BBBP
- Partner in implementation of Govt schmes
- Akshaya Patra Foundation to implement MDM
- Piramal Foundation for ADP
- Behavioural change–
- Lepra society (for leprosy patients), Snehalaya (for HIV infected)
- HelpAge India— Awareness on elderly care + campaigns for child’s R/S to take care of parents.
- ↑ Reach & penetration to untouched sections— Better conveying Govt message– Due to their proximity to masses
Role of NGOs in S-E Development
↑ Performance on Dev indicators & SDGs—↑ reach of Govt policies
- Education—Pratham (ASER), K.C. Mahindra Edu Trust ( Promote higher edu)
- Health— Public Health Foundation of India, Udaan welfare foundation—Help destitute—Cancer chemotherapy center.
- Paryas Society (NGO)— started ‘Asptal – Sansad Mobile Swasthya Seva’ initiative to provide free PHC in the remotest locations of Hamirpur constituency in HP.
- Women—Sewa, Sathin, Eklavya, Disha
- Env Protection—Greenpeace, WWF, TERI, Vanashakti NGO.
-
- Awareness campaigns, Plantation drives, promoting eco sustainable practices
-
- Protection & promotion of HRs
- Amnesty Intl
- Naz foundation—LGBT rights
- Women empowerment– Azad Foundation, Sewa, Sathin, Eklavya, Disha e
- Chetna, CRY & BBA—Child rights—works for street & working children
- Akshaya trust—To restore human dignity— Rehab, food & care to street destitute
- Navsarjan—Protect Dalit rights
- Samata– Protection of tribal rights
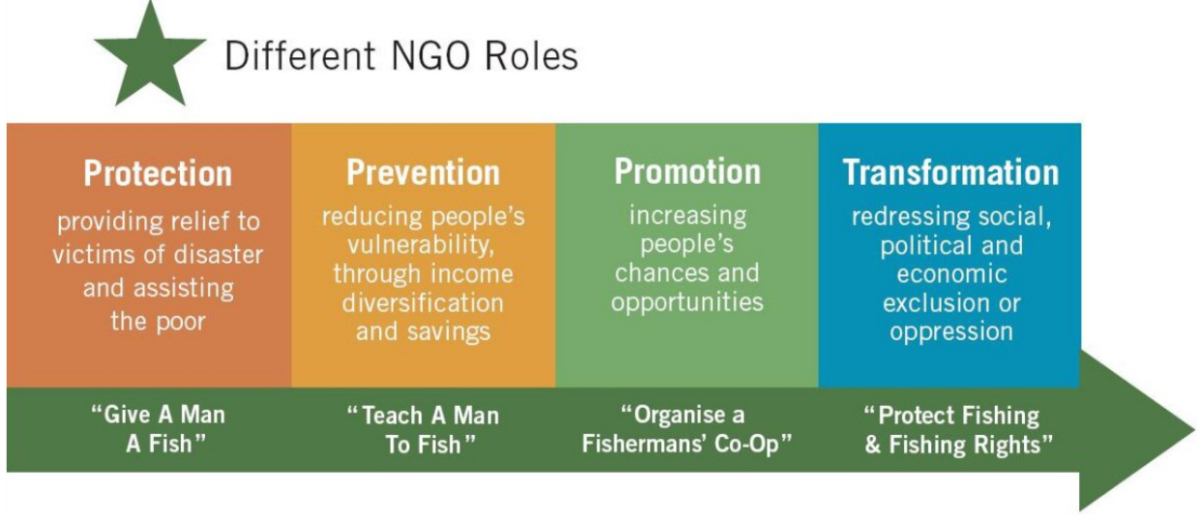
Issues & Challenges
- Non-A/C, Non-T/P & Undemocratic functioning—
- CBI report— <10% NGOs file annual financial statements
- Misappropriation of funds & Corruption
- Lack of T/P–> Doubt on ‘Genuineness’ of their non-profit spirit–> Aversion in donating funds
- Security Concerns ass with NGOs
- Org crime & Terror funding— NGO IRF accused of diverting funds for terrorism & radicalization.
- Conduits for Tax evasion & ML
- Foreign-funded NGOs tries to propagate foreign propaganda— Obstructionist activism— Stall Dev projects— Green Peace in Kudankulam Protest
- Create Hurdle in internal security— AFSPA opposed by Amnesty intl for HRs concerns.
- Thwats Democracy— manipulate election
- Undermining Development Activities
- IB Report– NGO activism reduces India’s GDP by 2-3% per year.
- Over-regulations—
- In 2018 cancelled licenses of nearly 20,000 NGOs receiving foreign funds under FCRA.
- Difficulties to get funds
- Cultural hurdles–Often seen as encroaching on culture. Ex– Protest Ban of Jallikattu after a PIL by PETA
Way Forward
- S. Vijay Kumar committee–
- “Light regulation” of NGOs— Need for a separate law for VOs
- Need for a nodal body to oversee the various interfaces b/w NGOs & Govt
- Modernise Registration procedures to facilitate seamless operation of IT Act & FCRA
- 2nd ARC & NPoVS 2007— Est a National Accreditation Council— to devise an accreditation system for VOs obtaining funds from Govt.
- Improving governance– Having a Board for governing NGO + Capacity building of staff
FCRA 2010
Objectives
- Regulate acceptance & utilization of foreign funds or hospitality + Prohibit their use for any activities detrimental to NI.
Recent actions
- Govt suspends FCRA clearance of 4 christian Groups
- Cancelled license of NGOs like—Sabrang Trust, Lawyer’s collective, Compassion Intl.
FCRA Amendment Bill 2020—
- Extended Prohibition to accept foreign contrib to P.S along with earlier—election candidates, judges, Govt servants, MP/MLAs etc
- Prohibits transfer of foreign funds to any other person (2010 act— can be transferred to person registered under FCRA)
- Aadhar of all office bearers mandatory for Registration or its renewal
- Now max 20% funds can be used for Adm purposes (2010 Act—50%)
- Govt may conduct an inquiry before renewing the certificate
- Foreign funds must be received only in an A/C designated by bank as “FCRA A/C” in notified branches of SBI, New Delhi.
- Mandatory renew of licence every 5 yr—↑ Govt’s discretion
Criticisms of FCRA
- Chilling effect on
- Freedom of free speech—Allowing only some political groups to receive foreign donations & disallowing others
- Freedom of ass under Art 19(1)(a) & 19(1)(c)
- May be used to target political opponents & religious minorities.
- As a tool to curb legitimate dissent —FCRA used as a tool of repression
- Sec 5 gives Union “unchecked & unbridled powers” to declare an org as of political nature & deny it access to foreign funds—Misused
Why amendment?
- To enhance T/P & A/C in receipt & utilisation of foreign contri + facilitating “genuine” NGOs which are working for welfare of society.
- Cut adm expenses to ensure that NGOs not use donations for personal use & to prevent siphoning of funds
Conclusion
- SC— A balance has to be drawn b/w the objectives of legislation & rights of VOs to have access to foreign funds.
Role of SHGs in Development
Introduction
- A ‘self-governed, peer controlled voluntory Ass of people with similar S-E background who aspire to improve their living stds & address their common problems’
- Origin—ROSCA (Rotating savingd & Credit Ass)—> Gained momentum after 1992 (SHG Bank Linkage Project)
Importance of SHGs
- Poverty alleviation & Rural Dev —
- Financial inclusion– Facilitates access to credit & Micro Finance to poors + SHGs members act as “Banking Correspondent” (Bank sakhi prog)
- Provide Livelihood (By vocational training, skill dev)– Improved living standards
- Promotes savings & investments
- Promotes Entrepreneurship—self-employment through setting of micro-enterprise
- Awareness generation + Efficacy in implementation of Govt schemes
- DAY-NRLM, MGNREGA
- Social Audits
- Many +ve externalities
- ↑ literacy, Nutrition– Operates PDS shops (MH)
- ↑ Maternal & Chilld health– By implementing ICDS & MDM
- Better health care, family planning
- Voice to marginalized—Social justice + Inclusive growth.
- Social Justice & Women empowerment–
- Financial independence through self-employment
- Encourages entrepreneurship
- Financial independence— ↑ Literacy rates, nutritional status– ↑ their self esteem
- Inculcates leadership skill—participate actively in gram sabha & elections
- SHGs bonds women into a collective force–> Act as PGs—Prohibition of liquor in Bihar bcz of pressure from women SHGs.
- Facilitate–
- Democratic Deepening & Grassroot empowerment ( Act as PGs at Village level)
- Creation of Social capital
- Combating Social ill— Close liquor shops
- Imbibing spirit of Self Help, Democracy, Social Solidarity & social cohesiveness
- Role of SHGs during COVID-19
- MoRD— 132 lakh+ masks were produced by 14.5 k SHGs
- Women SHG members (Bank Sakhis)— provided doorstep banking services— pensions etc
- Kudumbashree—Dispelling fake news + disseminating authentic information through WhatsApp groups + Delivered free ration + Running kitchens around state
- Prerna SHG (UP)—communicated on social distancing by street art & wall paintings.
Case studies
- Kudumbashree (Kerala)—Skill training & poverty eradication of women
- Sorath Mahila Vikas Mandali (Gir region) fighting social taboos by helping widows
- TN used SHGs to inculcate sanitation habits among people under SBM
- Haryana used for increasing sex ratio & BBBP
- SHGs like SEWA, Lizzat papad promotes entreprenurial culture among women.
- TANWA ( TN Women in Agri) by TN govt
Govt steps
- NABARD efforts–
- SHG-Bank Linkage Prog—For providing micro-finance / Collateral-free loans to SHGs.
- By providing grant for training, capacity building, skill upgradation.
- “Women SHGs Development Fund” (NABARD) with a corpus of 500 cr
- e-shakti initiative– for Digitisation of SHGs
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh—acts as a facilitating agency & provides loans to NGO-MFIs
- Budget 2019-20
- Women SHG interest subvention prog to be expanded to all districts
- Women SHG having a Jan dhan a/c to be allowed a overdraft of ₹5000.
- NRLM, DAY –NRLM— To promote self-employment in rural areas through formation & skilling of SHGs.
- Recent Announcement–
- To create 75 lakh SHGs by 2022
- 2x collateral free loans to WSHGs from 10 lakh to Rs 20 lakh.
Challenges for SHGs
- Socio-cultural hurdles—
- Embedded Patriarchy, Caste Rigidities
- Illiteracy— Information asymmetry
- Lack of financial literacy—Creates Mgt & Governance issues
- Lack of proper training regarding production tech, quality, packing, etc—No competitive adv.
- Problems related to Raw Materials, Marketing—Bcz of
- Lack of linkages with marketing agencies
- Inadequate sales promotion
- Issues of quality & Tough Competition
- 2nd ARC
- Most of their activities are still based on primitive skills related mostly to primary sector enterprises—Poor value addition—No substantial increase in the income of group members
- SHG has led to definite social empowerment of poors but economic gains rnot adequate to bring a qualitative change in their life.
Way forward
- Est separate SHG monitoring cell in every state
- Awareness camps about schemes of assistance available to SHSGs
- Invest in digital-financial literacy & Entrepreneurship Dev
- With increasing Urban poors—Need to develop & strengthen SHG network in urban areas.
- 2nd ARC—SHGs needs to be extended to urban & peri-urban areas
SHGs are imperative for economic revival & reconstruction in post covid order

![UPSC CSE Topper Mains Answer [Part 2] images-2023-06-17T192027.770](https://iasbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/images-2023-06-17T192027.770-150x150.jpeg)




![UPSC CSE Topper Mains Answer [Gaurav Agarwal] word-image-10753-1](https://iasbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/word-image-10753-1-150x150.png)







